Canon pioneered the adoption of CMOS sensors in mainstream cameras. In 2000, the EOS D30 digital SLR debuted Canon’s first self-developed APS-C CMOS sensor (3.25MP). By 2016, models like the 1DX Mark II, 80D, and 5D Mark IV featured integrated ADCs for enhanced dynamic range. In 2020, the EOS R5 and 2021’s EOS R3 showcased Canon’s latest stacked CMOS technology, including a 24MP full-frame sensor.
With over 80 years of imaging expertise, Canon remains committed to in-house R&D for critical components. Since 2000, Canon has developed CMOS sensors for diverse applications, achieving milestones such as:
250MP APS-H CMOS sensor
120MP high-resolution CMOS sensor
19MP global shutter CMOS sensor
I. CCD vs. CMOS Image Sensors
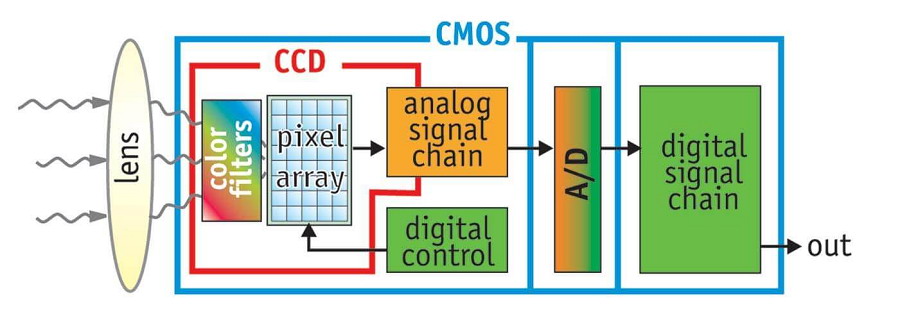
Figure 1: CCD vs. CMOS Sensor Differences
CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) sensors dominated consumer and high-end markets from the 1980s until CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor) emerged as a cost-effective alternative post-2008. Today, CMOS sensors are ubiquitous in smartphones, automotive systems, medical devices, DSLRs, and more.
CMOS Working Principle:
A CMOS sensor uses silicon and germanium semiconductors with N/P junctions. The complementary electrical currents generated by light exposure are processed into digital images.
1.1 Core Technical Specifications
| Parameter | Definition |
| Effective Pixels | Total active pixels determining resolution and clarity. |
| Pixel Size (μm) | Smaller pixels enable higher resolution but reduce light sensitivity. |
| Optical Format (in) | Diagonal sensor size; larger formats improve light capture and SNR. |
| Frame Rate (fps) | Frames per second, critical for video smoothness and motion capture. |
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio; higher values yield cleaner images. |
| Dynamic Range (dB) | Peak signal vs. noise ratio, reflecting signal processing capability. |
| Sensitivity (V/lux·s) | Light response efficiency, measured as current responsivity. |
| Quantum Efficiency | Photon-to-electron conversion rate; higher QE improves brightness and SNR. |
1.2 Shutter Types
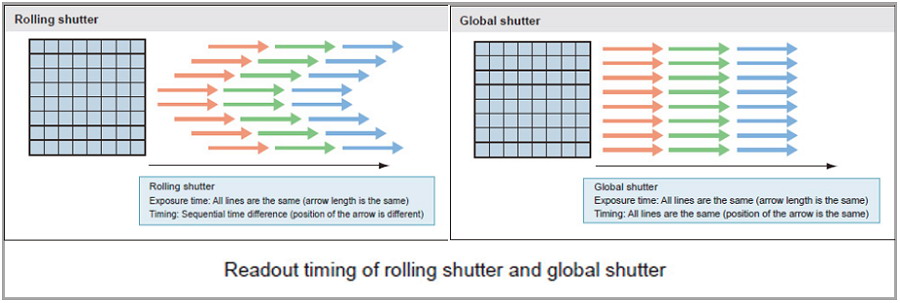
Figure 2: Rolling vs. Global Shutter
Rolling Shutter (RS):
Exposes rows sequentially, causing motion distortion (e.g., skewing fast-moving objects).
Global Shutter (GS):
Simultaneous exposure for all pixels, eliminating distortion at higher cost and complexity.
1.3 Sensor Architectures
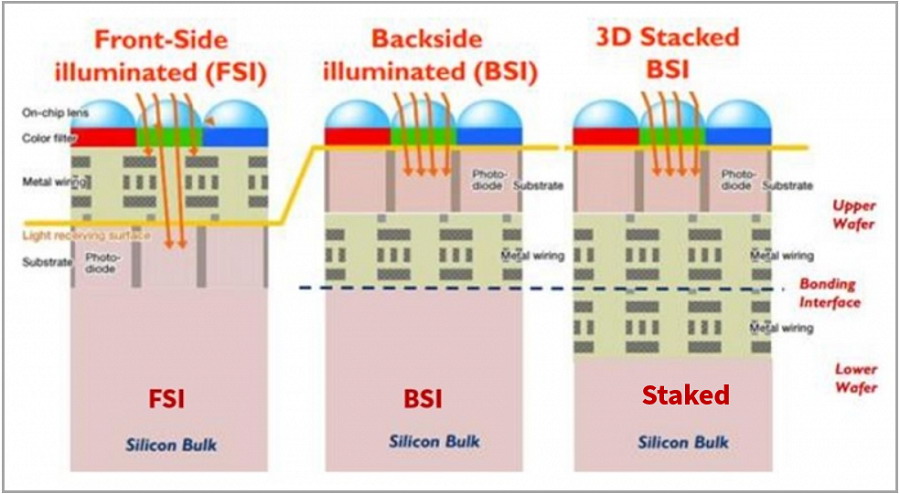
Figure 3: CMOS Sensor Structures
Front-Side Illumination (FSI):
Traditional design with light passing through metal wiring layers, causing light loss.
Back-Side Illumination (BSI):
Places photodiodes above wiring for improved light capture; dominant in mid-to-high-end sensors.
Stacked BSI:
Further optimizes BSI by relocating logic circuits below photodiodes, reducing size and enhancing image quality.
II. Canon CMOS Sensor Highlights
Canon’s China-market sensors span high-resolution, global shutter, and general-purpose categories, covering optical formats from 1/1.8" to full-frame.
2.1 410MP Full-Frame Back-Illuminated Stacked CMOS
Resolution: 24,592 x 16,704 pixels (198x 1080p, 12.4x 8K).
Speed: 3.28 billion pixels/sec readout (8 fps video at 410MP, 24 fps at 100MP).
Applications: Security, medical imaging, industrial inspection.

Figure 4: 410MP Full-Frame BSI CMOS Sensor
2.2 250MP APS-H CMOS Sensors (LI8020SAC/LI8020SAM)
Resolution: 250MP for 4K/8K applications in display inspection, film production, and surveillance.
Speed: 1.25 billion pixels/sec (5 fps full-resolution, 24 fps 8K, 30 fps 4K).
ROI Feature: Partial readout for higher frame rates.
2.3 120MP RGB-IR Sensor (LI8010SAI)
APS-H Format: 29.22 x 20.20 mm, 2.2μm pixels.
Dual Spectrum: Captures visible + near-infrared (NIR) light via RGIRB filter.
Applications: Food inspection (spoilage detection), medical diagnostics (vein imaging).

Figure 5: Visible + NIR Imaging
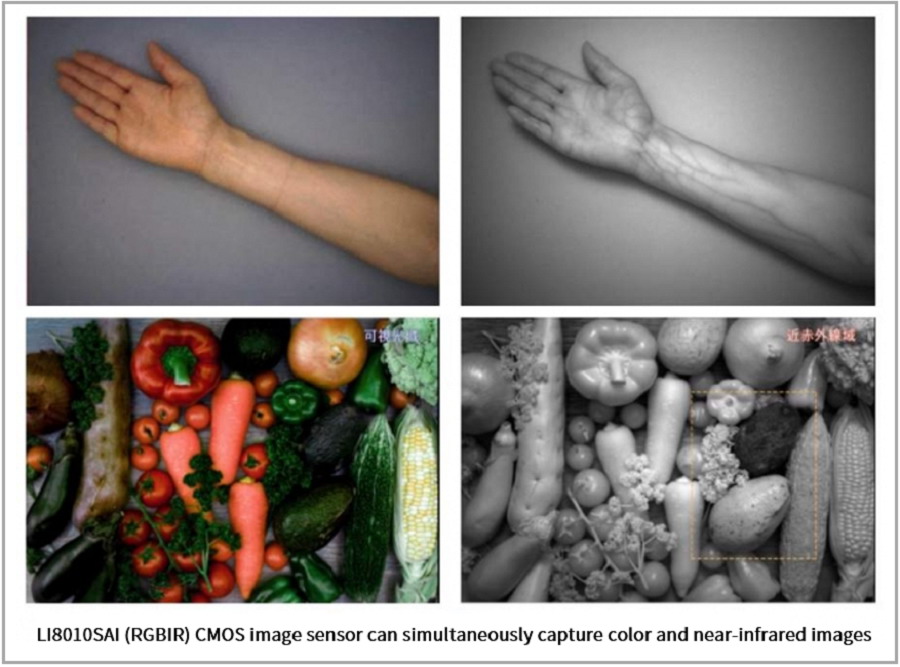
Figure 6: Medical/Industrial Use Cases
2.4 19MP Global Shutter CMOS (LI5030SA Series)
Variants: Color (LI5030SAC), monochrome (LI5030SAM), NIR (LI5030SAI), and bare (LI5030SAN).
Performance: 58 fps at 19MP (5688 x 3334), ideal for microscopy and traffic monitoring.
III. Canon CMOS Sensor Portfolio
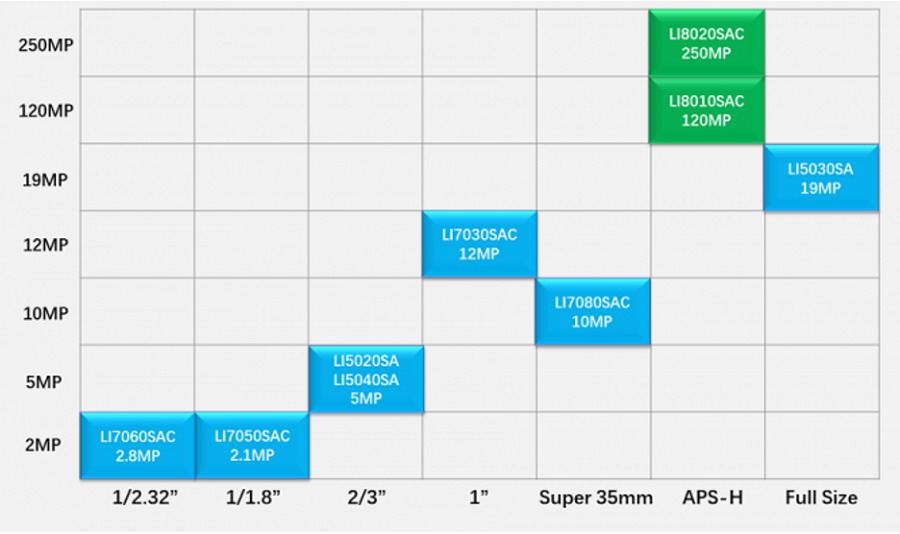
Figure 7: Canon’s High-Performance CMOS Series
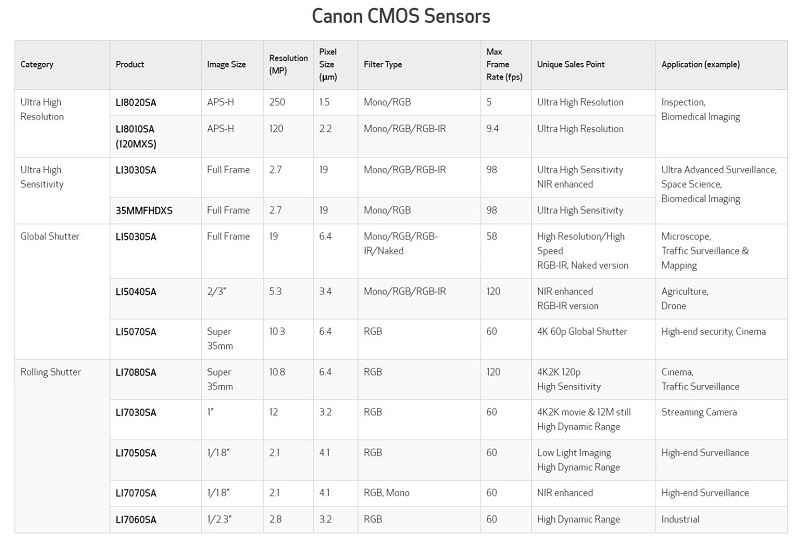
Figure 8: Canon CMOS Selection Guide
Contact Us:
For detailed technical specifications or sampling requests, please contact us.









