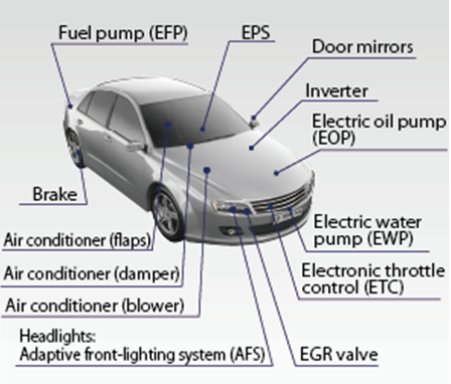
Toshiba delivers a comprehensive portfolio of semiconductors essential for automotive electrification, focusing on automotive inverters, battery management systems (BMS), and motor drivers for applications such as electric power steering, electric water pumps, and HVAC fans. The company excels in high-voltage, low-loss power devices. Moving forward, Toshiba will continue to pioneer cutting-edge semiconductor technologies to meet tomorrow’s automotive demands.
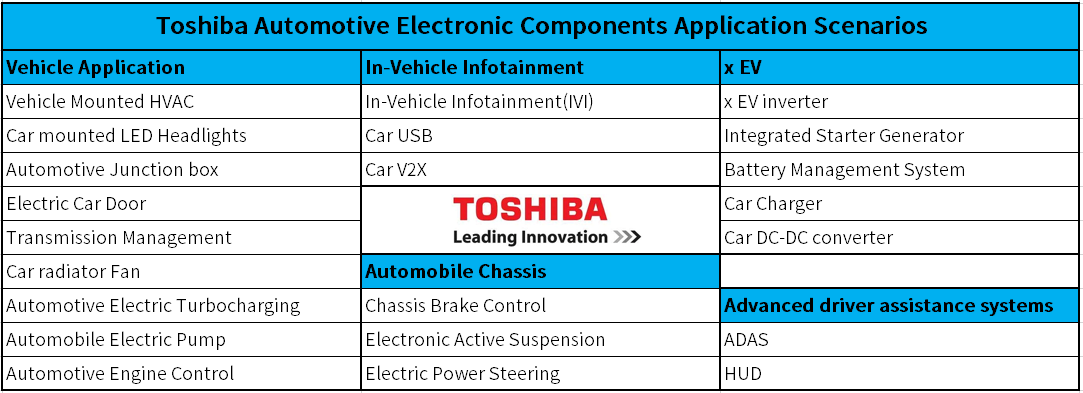
Figure 1: Application Scenarios for Toshiba Automotive Discrete Devices
I. Automotive Discrete Semiconductors (AEC-Q101 Compliant)
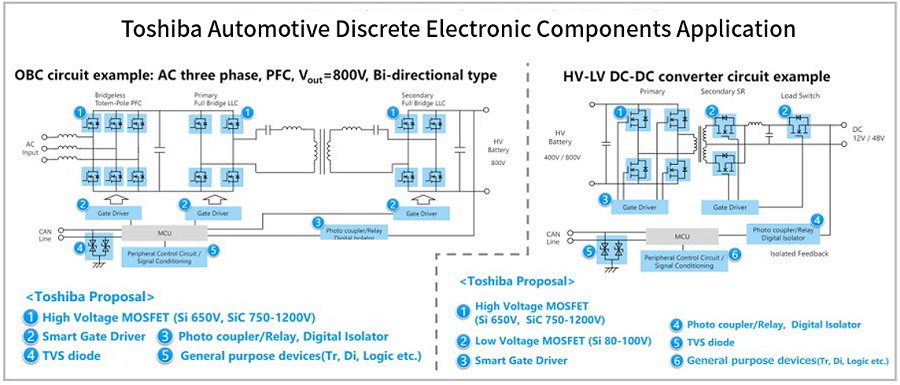
Figure 2: Toshiba Automotive Discrete Device Applications
1.1 Automotive MOSFETs
Toshiba offers a broad lineup of power MOSFETs covering various automotive applications in 12V to 48V battery systems. Leveraging advanced wafer processing technologies developed by Toshiba to suppress switching noise, combined with low-resistance packaging techniques, these devices achieve industry-leading low on-resistance, reduced power loss, and miniaturization.
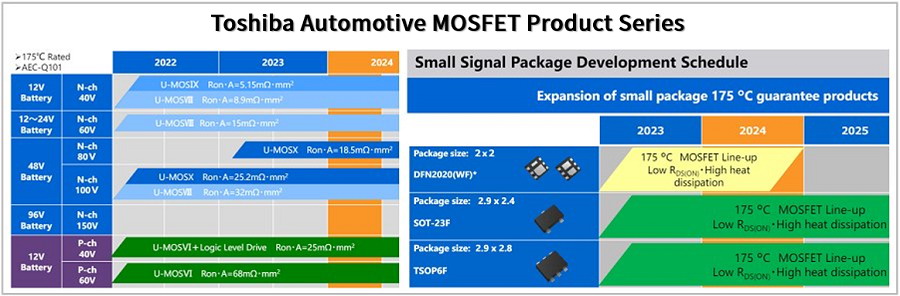
Figure 3: Toshiba’s AEC-Q101 Mid/Low-Voltage MOSFETs and Compact Packages
1.2 Automotive Opto-Couplers
These integrate a high-output LED chip and a high-gain photodetector, enhancing safety and stability through redundant communication. Compact designs minimize PCB footprint.
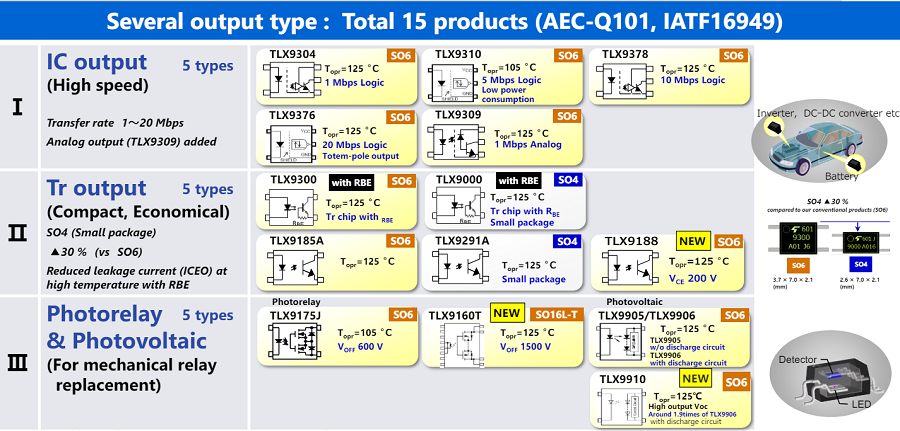
Figure 4: Toshiba Automotive Opto-Coupler Series
1.3 Automotive Photorelays (MOSFET Output)
Non-contact relays enable energy savings and extended equipment lifespan. By combining opto-couplers with MOSFETs, Toshiba delivers ideal contactless relay solutions.
II. Automotive Diodes (AEC-Q101 Compliant)
2.1 Automotive TVS Diodes (ESD Protection Diodes)
As ESD and surge protection for automotive ECUs grows critical, Toshiba’s TVS diodes safeguard against transient voltages, preventing damage from electrostatic discharge. The lineup spans CAN/LIN interface protection to LVDS high-speed signal protection.
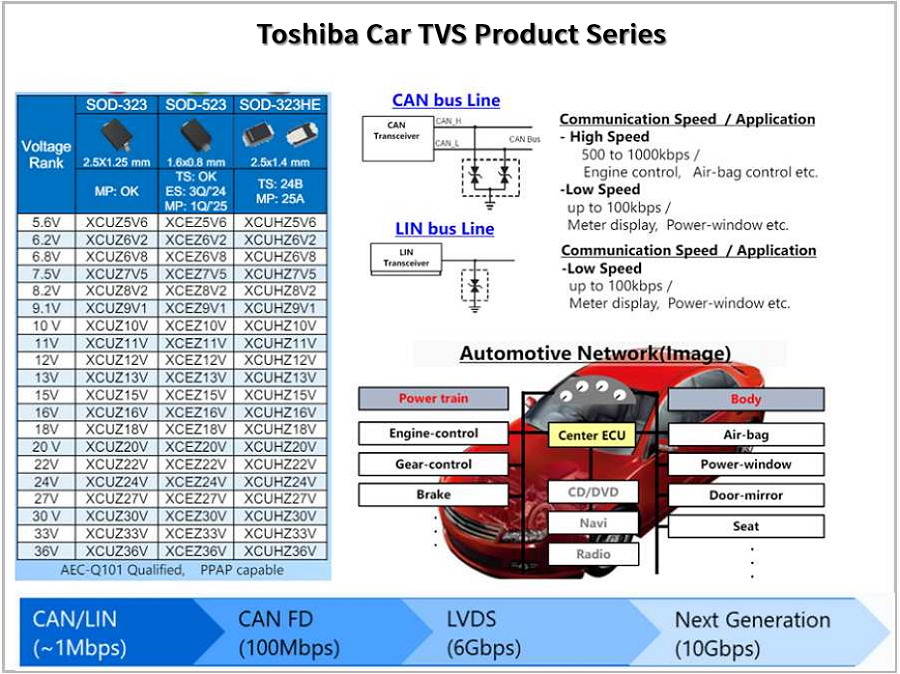
Figure 5: Toshiba’s High-Performance Automotive TVS Devices
2.2 Automotive Schottky Diodes
Reverse voltage ratings: 20–60V.
2.3 Automotive Rectifier Diodes
Surface-mount packages with reverse voltages of 200–1000V and forward currents of 0.5–3A.
2.4 Automotive Switching Diodes
Multiple voltage ratings and compact packages to meet diverse needs.
2.5 Automotive Zener Diodes
Zener voltage range: 6.2–82V.
III. Automotive Transistors (AEC-Q101 Compliant)
3.1 Automotive Bipolar Transistors
Toshiba’s portfolio includes ultra-compact small-signal transistors and medium-packaged power transistors (low-saturation/high-current types).
3.2 Bias Resistor Transistors (BRTs)
Available in small packages with varied resistor configurations.
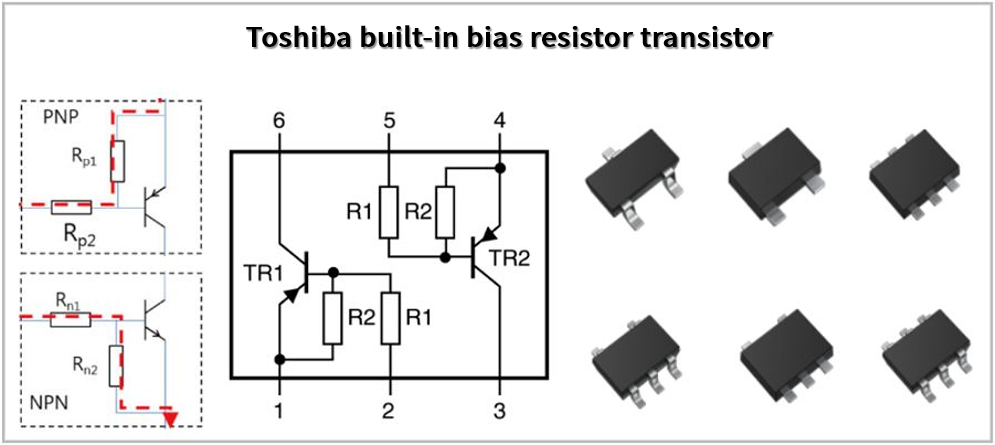
Figure 6: Toshiba’s AEC-Q101 BRTs
IV. Automotive Analog Devices (AEC-Q100 Compliant)
Toshiba’s 0.13μm BiCD process integrates analog circuits with large-scale logic and power (DMOS) devices on a single chip, enabling reduced system size and power consumption. As EVs and HEVs advance, demand grows for motor control and power electronics. Toshiba provides analog devices with wide voltage/current ratings and proven applications.
4.1 Brushless Motor Driver ICs
Electric Pumps: Sensorless control with hardware logic.
HVAC Fans: Silent, efficient sine-wave control.
EPS Systems: Functional safety-compliant sensor inputs.
4.2 Brushed Motor Driver ICs
H-bridge drivers with low Rds(on) MOSFETs, LIN support, and high heat dissipation (5A rating).
4.3 Stepper Motor Driver ICs
Feature micro-stepping for noise/vibration reduction, stall detection, and AEC-Q100 compliance.
4.4 Intelligent Power Devices (IPD)
High-side/low-side switches and MOSFET gate drivers with integrated protection/diagnostic functions for ADAS and body control.
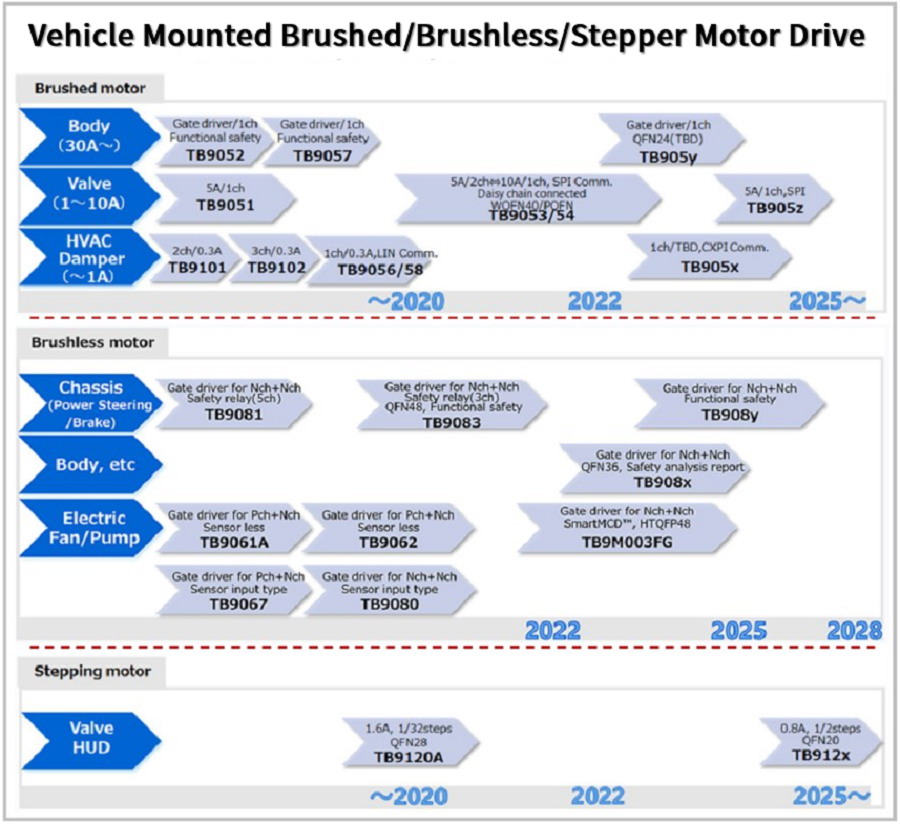
Figure 7: Toshiba’s Automotive Brushed/Brushless/Stepper Motor Driver IC Series
4.5 System Power ICs
DC-DC converters with functional safety for high-current, multi-output automotive systems (e.g., EPS).
4.6 Audio Power Amplifiers
Advanced 0.13μm process enables Class-TB efficiency (comparable to Class-D) with low power consumption and robust protection.
4.7 In-Vehicle Networking
Supports evolving protocols like CXPI for body systems and Ethernet TSN for ADAS/autonomous driving.
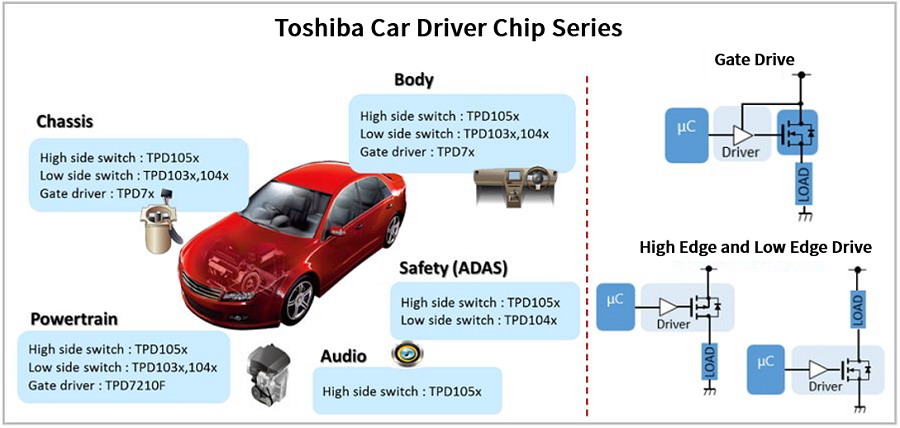
Figure 8: Toshiba Automotive Driver ICs
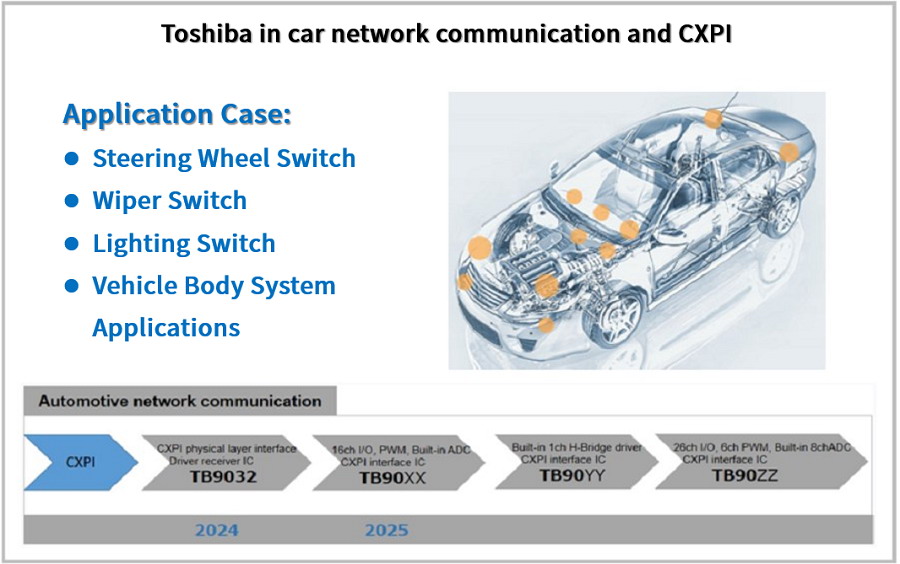
Figure 9: Toshiba Automotive Networking Solutions
V. Automotive Logic ICs (AEC-Q100 Compliant)
5.1 CMOS Logic ICs
Low-voltage and high-speed variants in industry-standard packages.
5.2 Single-Gate Logic ICs (L-MOS)
Compact packages for diverse requirements.
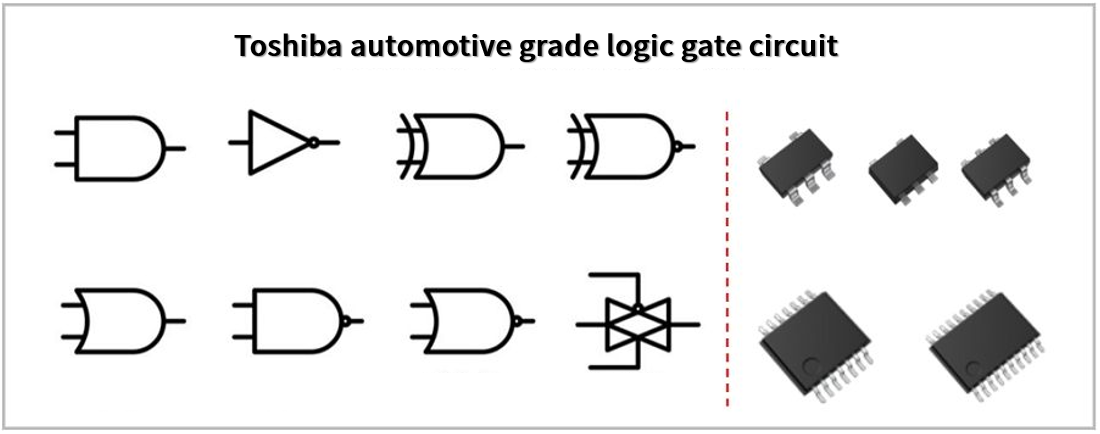
Figure 10: Toshiba AEC-Q100 CMOS Logic Gates
VI. Automotive Digital Devices
6.1 Video Processor ICs
Enhance visibility for automotive displays with stable synchronization and image quality tuning.
6.2 Video Decoder ICs
Convert analog (CVBS) to digital formats (BT.656) with edge enhancement and dynamic gamma.
6.3 Bridge ICs
Peripheral Bridge ICs: Resolve interface mismatches between legacy peripherals and modern SoCs.
Ethernet Bridge ICs: Enable low-latency AVB/TSN networks for ADAS.
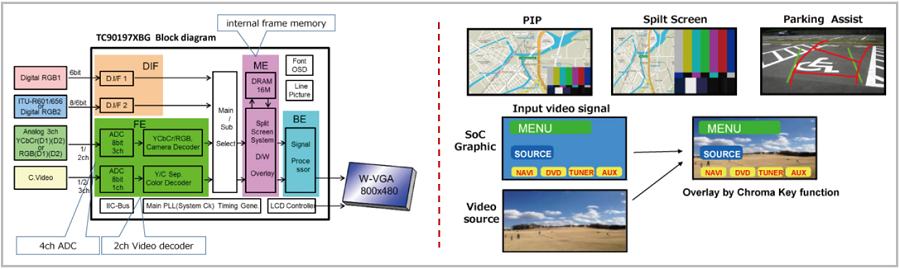
Figure 11: Toshiba Automotive Video Processors
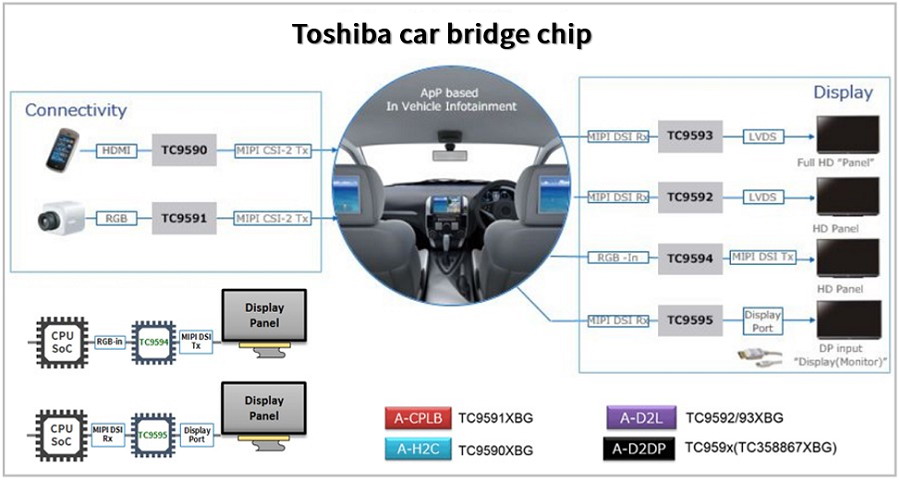
Figure 12: Toshiba Peripheral Bridge IC Applications
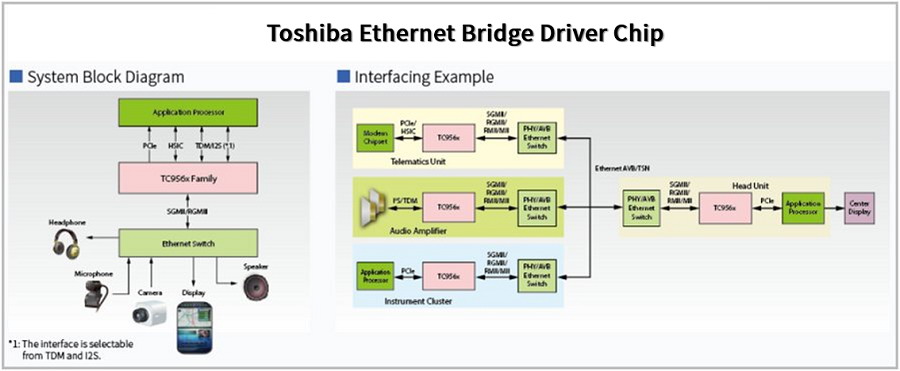
Figure 13: Toshiba Ethernet Bridge ICs
VII. Wireless Devices
Automotive Wireless Communication ICs
Support ETC, RKE, TPMS, and roadside infrastructure.
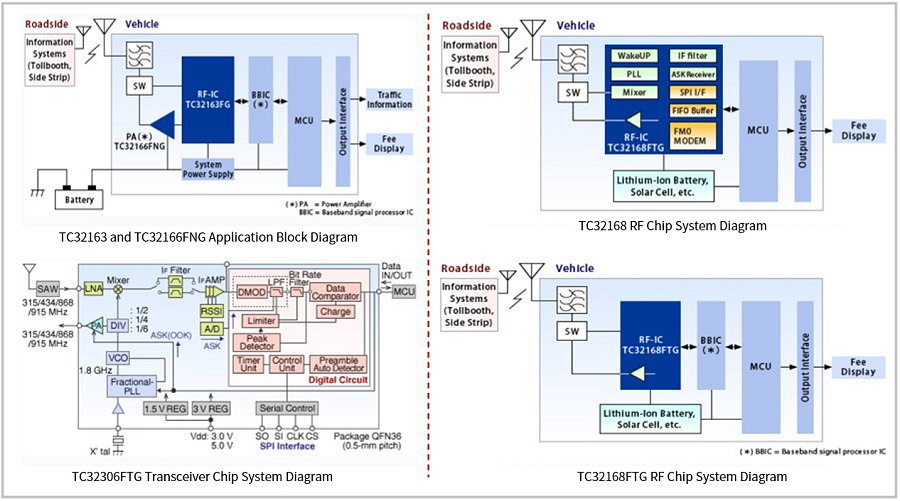
Figure 14: Toshiba Automotive Communication ICs